Workshop Cranes
1. What is a Workshop Crane?
A workshop crane is a material handling device designed for lifting, moving, and positioning heavy loads in industrial, automotive, and manufacturing environments. Unlike large industrial cranes, workshop cranes are typically smaller, more versatile, and optimized for confined workspaces.
Key Characteristics of Workshop Cranes:
✔ Compact & Space-Efficient – Designed for workshops with limited space.
✔ Versatile Load Handling – Used for machinery, engines, construction materials, and more.
✔ Manual or Powered Operation – Some use hydraulic/electric systems, while others are hand-operated.
✔ Enhanced Safety – Reduces manual lifting risks and improves workplace efficiency.
2. Types of Workshop Cranes & Their Applications
(1) Mobile Workshop Cranes (Portable Cranes)
Definition:
A mobile crane is a wheel-mounted lifting device that can be easily moved around the workshop. It typically has an adjustable boom and hydraulic or manual lifting mechanisms.
Applications:
🔹 Automotive Workshops – Lifting engines, transmissions, and vehicle parts.
🔹 Maintenance & Repair – Moving heavy machinery for servicing.
🔹 Small Manufacturing – Handling materials in tight spaces.
Advantages:
✅ Easy to reposition
✅ No fixed installation required
✅ Cost-effective for small to medium lifting tasks
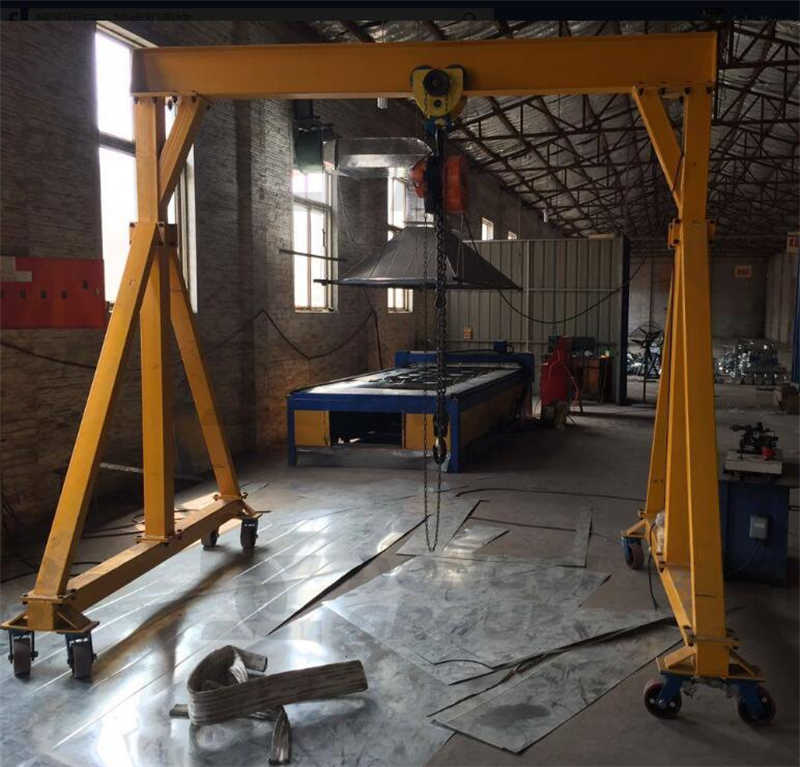

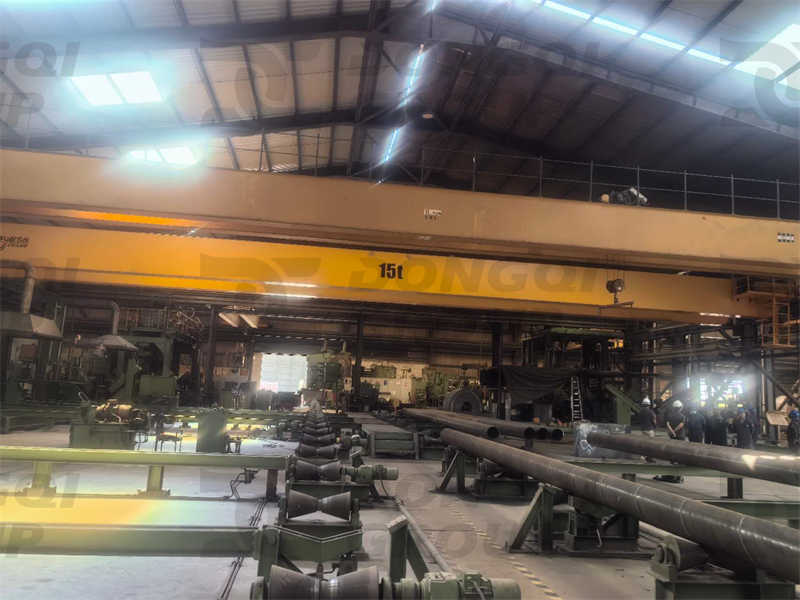
(2) Overhead Workshop Cranes (Bridge Cranes)
Definition:
An overhead crane consists of a horizontal beam (bridge) that moves along elevated runways, allowing lifting across a wide area.
Types:
- Single-Girder Overhead Crane (Light to medium loads, 1-20 tons)
- Double-Girder Overhead Crane (Heavy-duty, 20-100+ tons)
Applications:
🔹 Manufacturing Plants – Assembly line lifting.
🔹 Warehouses – Moving pallets and heavy inventory.
🔹 Metal Fabrication – Handling steel beams and large components.
Advantages:
✅ Maximizes floor space (no ground obstructions)
✅ High lifting capacity
✅ Smooth and precise load control

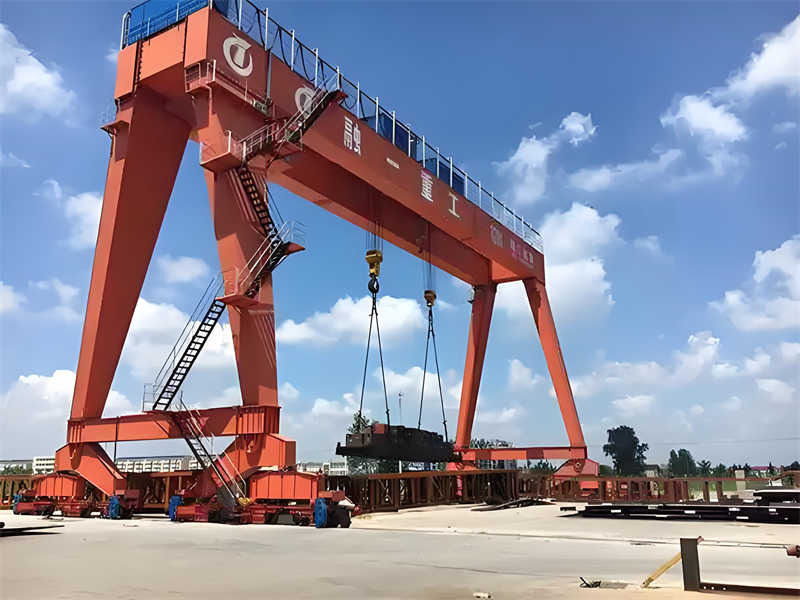
(3) Workshop Gantry Cranes (Freestanding Cranes)
Definition:
A gantry crane is a freestanding structure with a horizontal beam supported by two legs. Unlike overhead cranes, it doesn’t require ceiling mounting.
Types:
- Fixed Gantry Crane (Permanent installation)
- Mobile Gantry Crane (Wheeled for repositioning)
Applications:
🔹 Shipbuilding & Dockyards – Lifting heavy ship parts.
🔹 Construction Sites – Moving steel beams and concrete panels.
🔹 Outdoor Workshops – Where overhead support is unavailable.
Advantages:
✅ No need for ceiling support
✅ Can be used indoors and outdoors
✅ Adjustable span and height

(4) Small Workshop Cranes (Jib Cranes & Mini Cranes)
Definition:
A small workshop crane is a compact lifting device, often wall-mounted or floor-standing, designed for light to medium loads.
Types:
- Wall-Mounted Jib Crane (Space-saving, 0.5-5 tons)
- Free-Standing Jib Crane (No wall support needed, 1-10 tons)
Applications:
🔹 CNC Machining Centers – Loading/unloading workpieces.
🔹 Auto Repair Shops – Lifting small engines and parts.
🔹 Laboratories & Workshops – Handling delicate equipment.
Advantages:
✅ Ideal for tight spaces
✅ Quick and easy operation
✅ Low maintenance

(5) Articulating Workshop Cranes (Flexible Arm Cranes)
Definition:
An articulating crane has a rotating boom with multiple pivot points, allowing precise load positioning in tight spaces.
Applications:
🔹 Aerospace Industry – Installing aircraft components.
🔹 Assembly Lines – Positioning machinery parts with precision.
🔹 Cleanroom Environments – Handling sensitive materials.
Advantages:
✅ 360° rotation for flexible movement
✅ Ideal for awkwardly shaped loads
✅ Reduces worker strain
3.How to Choose the Right Workshop Crane
Selecting the ideal workshop crane requires careful consideration of several key factors. Below is a detailed breakdown to help you make an informed decision:
1. Determine Your Lifting Requirements
(1) Maximum Load Capacity
- Assess the heaviest load you need to lift regularly
- Choose a crane with 20-30% more capacity than your maximum requirement for safety
- Typical workshop crane capacities:
- Small jib cranes: 0.5-5 tons
- Mobile cranes: 1-10 tons
- Overhead cranes: 1-100+ tons
(2) Lifting Height & Span
- Measure:
- Vertical lifting height required
- Horizontal movement distance (span)
- Clearance needed under ceilings (for overhead cranes)
(3) Duty Cycle & Frequency of Use
- Light duty: Occasional use (e.g., <10 lifts/day)
- Medium duty: Regular operation (e.g., 10-20 lifts/day)
- Heavy duty: Continuous operation (e.g., >20 lifts/day)
2. Evaluate Your Workspace Conditions
(1) Available Space
| Space Type | Recommended Crane |
|---|---|
| Small, confined area | Wall-mounted jib crane or small mobile crane |
| Large open area | Gantry crane or overhead crane |
| Limited ceiling height | Low-headroom overhead crane |
(2) Floor & Structural Considerations
- Floor strength: Can it support crane + load?
- Ceiling structure: Strong enough for overhead crane?
- Obstructions: Columns, machinery, or doorways that limit movement
(3) Indoor vs Outdoor Use
- Outdoor cranes: Require weather-resistant materials (stainless steel, special coatings)
- Indoor cranes: Standard materials usually sufficient
3. Select the Appropriate Crane Type
| Crane Type | Best For | Not Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Crane | Flexible movement needs; small-medium loads | Heavy, continuous lifting |
| Overhead Crane | High-precision lifting; maximizing floor space | Workshops with weak ceiling structures |
| Gantry Crane | Outdoor/indoor use without ceiling support | Very small workspaces |
| Jib Crane | Repetitive light lifting in confined areas | Large/heavy loads |
4. Choose the Right Power & Control System
(1) Power Options
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Low cost; simple maintenance | Physically demanding; slower operation |
| Electric | Smooth operation; precise control | Higher initial cost |
| Hydraulic | Powerful; good for heavy loads | Requires maintenance |
| Pneumatic | Clean operation (good for labs) | Limited power |
(2) Control Methods
- Pendant control: Basic wired remote
- Radio remote: Wireless operation (better visibility)
- Cab-operated: For very large cranes
5. Consider Safety & Compliance
(1) Essential Safety Features
✔ Overload protection
✔ Emergency stop button
✔ Limit switches
✔ Anti-collision systems (for multiple cranes)
(2) Compliance Standards
- ISO 9001: Quality management
- CE/ASME: Safety certifications
- OSHA/ANSI: Workplace safety regulations
6. Budget & Long-Term Costs
| Cost Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Initial purchase | Mobile cranes typically cheapest; overhead cranes most expensive |
| Installation | Overhead cranes require structural modifications |
| Maintenance | Electric cranes have lower maintenance than hydraulic |
| Energy costs | Electric vs hydraulic power consumption |
7. Dongqi Crane Selection Checklist
✅ [ ] Confirmed maximum load weight
✅ [ ] Measured workspace dimensions
✅ [ ] Determined indoor/outdoor use
✅ [ ] Selected appropriate crane type
✅ [ ] Chosen power/control system
✅ [ ] Verified safety requirements
✅ [ ] Budget accounted for total cost of ownership
Still unsure? Contact Dongqi Crane’s experts for a free consultation and site evaluation!
4. Why Choose Dongqi Crane?
✔ Custom Solutions – Tailored designs for your workshop needs.
✔ High-Quality & Durable – ISO-certified manufacturing.
✔ Global Supplier – Reliable service in Australia, Europe, and beyond.
Need a Workshop Crane? Contact Dongqi Crane today for expert advice and a free quote!